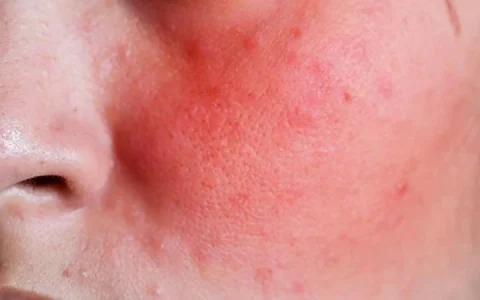
What is rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic disorder of the facial skin. It usually appears as redness on the cheeks, nose, chin or forehead. The redness tends to become more persistent with time, and tiny blood vessels and small bumps often develop. In patients with severe chronic rosacea, their noses may swell and become lumpy (rhinophyma). Sometimes, the eyes are also affected and may be watery or bloodshot.
What can trigger or worsen rosacea?
Exposure to sunlight and consuming alcoholic drinks, spicy foods, and hot drinks such as coffee and tea can cause flushing and trigger rosacea. Other triggers include exercise, certain medication, stress, anxiety and temperature extremes. The use of topical steroids on the face can worsen the condition. Demodex mites are thought to be one of the causes of rosacea. Strong drying facial washes, fragrances, acetone or alcohol-containing hair sprays and cosmetics can irritate the skin.
How is rosacea treated?
It is important to avoid any known triggers that can aggravate your rosacea. The treatment of rosacea can be divided into 3 main groups; topical treatment, oral medication, and light and laser treatment. Your dermatologist will propose the best treatment plan after a detailed consultation and examination.