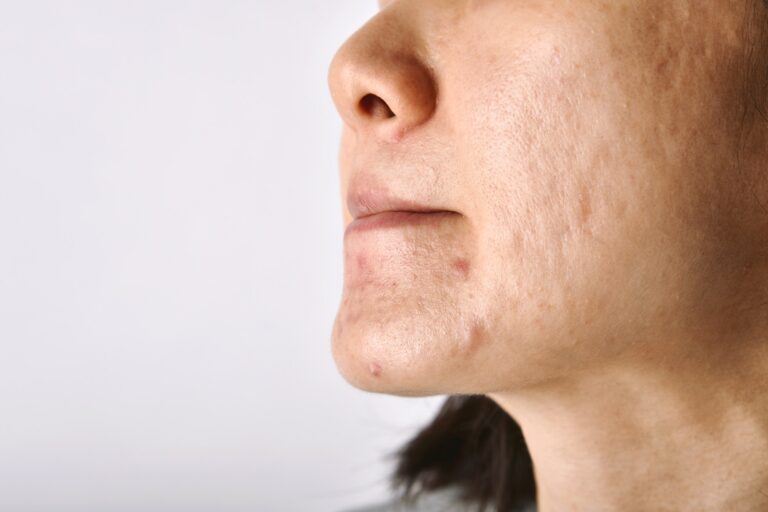
Acne Scars Skin Treatment
Many patients who have moderate to severe acne will have some degree of acne scarring. More severe, chronic and deeper inflammation is more likely to result in acne scars.

Many patients who have moderate to severe acne will have some degree of acne scarring. More severe, chronic and deeper inflammation is more likely to result in acne scars.

Acne can be a concern at many ages. It is a condition that develops in and around the hair follicles and their oil-producing glands called the sebaceous glands. Acne usually develops on the face, chest and back.

Actinic keratosis (AK) or solar keratosis is a precancerous skin lesion that appears on chronically sun-damaged skin. They usually appear as small pink crusty or scaly patches on sun-exposed skin.

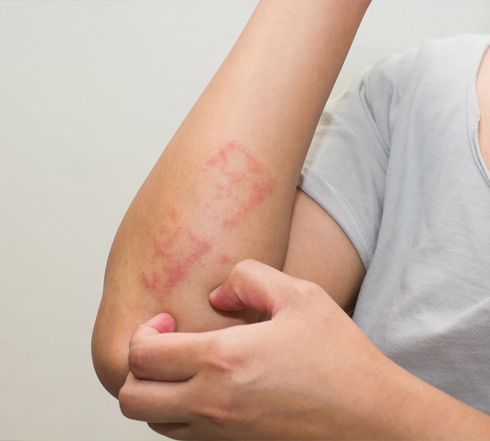
Atopic eczema is a very common skin condition which causes a dry, itchy and red rash. The term ‘eczema’ is used interchangeably with ‘dermatitis’ and refers to inflammation of the skin. It is common in babies and children but can occur at any age.
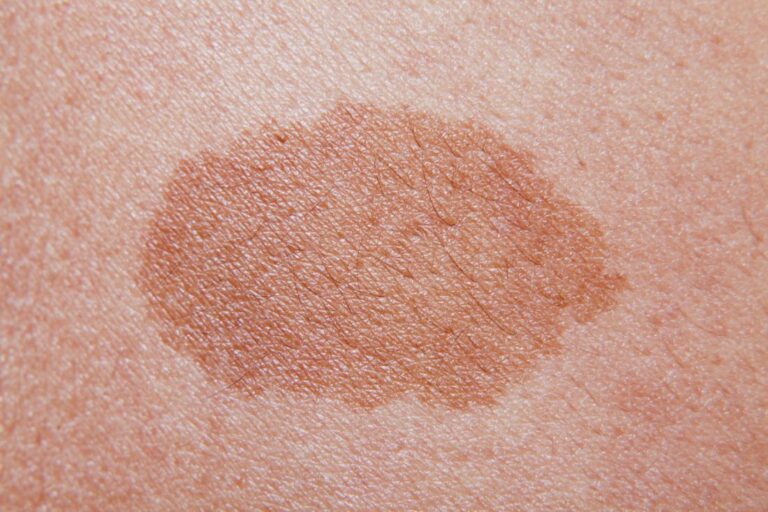

A birthmark appears as a spot, patch, or lump that looks different from the rest of your baby’s skin. You may see this when your baby is born or shortly after birth. Some birthmarks become more visible when your child is older or even during adolescence.

Contact allergy is a sensitivity reaction of the skin that some of us may develop on contact with substances usually harmless to others. These substances, or allergens as they are called, can enter the skin and cause the skin to break out with a rash.



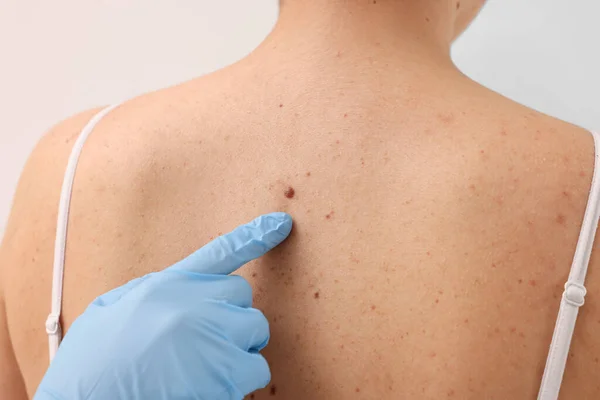
A mole is a benign collection of melanocytes. Melanocytes or pigment-producing cells in our skin. Moles usually appear as regular brown spots of varying sizes. Their colour can range from.

Our nails may look abnormal due to various reasons. Some common causes of nail changes include nail trauma, bacterial or fungal nail infection and an associated skin condition such as psoriasis.

These are small light-brown flat spots on sun-exposed skin such as the cheeks and nose. They may appear in childhood or adolescence and increase in number with age. Freckles may lighten with reduced sun exposure and with the use of broad-spectrum sunscreen.


Skin infections can be caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. Skin infestations can be caused by parasites. Here are some common skin infections in adults and children.
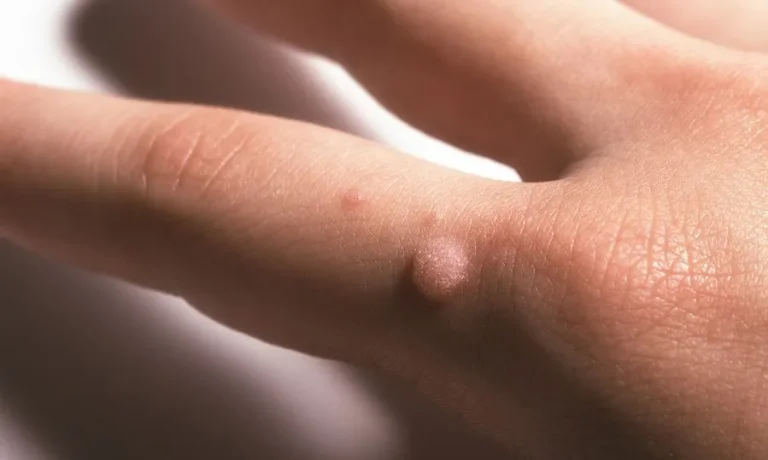
Viral warts are skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus. Warts can grow on any part of the body including the face, fingers and feet. Warts have a rough surface on which tiny, dark dots can often be seen.